**Side-channel attacks** are attacks based on information collected...
### Multipath Signals
When wireless signals propagate away from th...
Alipay is an incredibly popular payment platform. In 2015 it proces...
#### Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
ICMP is an internet ...
The main idea of **Principal Component Analysis** is that you have ...
**MIMO (multiple input, multiple output)** is a technique in wirele...
**OFDM (Ortogonal frequency-division multiplexing)** is a method in...
The Intel 5300 NIC costs about 5 USD and the directional antenas us...
This seems like a particularly interesting insight. Alipay is certa...
At first it might seem that this distance requirement would make it...
When CSI Meets Public WiFi: Inferring Your Mobile Phone
Password via WiFi Signals
Mengyuan Li
1
, Yan Meng
1
, Junyi Liu
1
, Haojin Zhu
1∗
, Xiaohui Liang
2
,
Yao Liu
3
and Na Ruan
1
1
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
2
University of Massachusetts at Boston
3
University of South Florida
ABSTRACT
In this study, we present WindTalker, a novel and practi-
cal keystroke inference framework that allows an attacker
to infer the sensitive keystrokes on a mobile device through
WiFi-based side-channel information. WindTalker is moti-
vated from the observation that keystrokes on mobile devices
will lead to different hand coverage and the finger motions,
which will introduce a unique interference to the multi-path
signals and can be reflected by the channel state informa-
tion (CSI). The adversary can exploit the strong correlation
between the CSI fluctuation and the keystrokes to infer the
user’s number input. WindTalker presents a novel approach
to collect the target’s CSI data by deploying a public WiFi
hotspot. Compared with the previous keystroke inference
approach, WindTalker neither deploys external devices close
to the target device nor compromises the target device. In-
stead, it utilizes the public WiFi to collect user’s CSI data,
which is easy-to-deploy and difficult-to-detect. In addition,
it jointly analyzes the traffic and the CSI to launch the
keystroke inference only for the sensitive period where pass-
word entering occurs. WindTalker can be launched without
the requirement of visually seeing the smart phone user’s in-
put process, backside motion, or installing any malware on
the tablet. We implemented Windtalker on several mobile
phones and performed a detailed case study to evaluate the
practicality of the password inference towards Alipay, the
largest mobile payment platform in the world. The evalua-
tion results show that the attacker can recover the key with
a high successful rate.
Keywords
Password Inference; Channel State Information; Online Pay-
ment; Wireless Security; Traffic Analysis
∗
Corresponding author, Email: zhu-hj@cs.sjtu.edu.cn
Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or
classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed
for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full cita-
tion on the first page. Copyrights for components of this work owned by others than
ACM must be honored. Abstracting with credit is permitted. To copy otherwise, or re-
publish, to post on servers or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission
and/or a fee. Request permissions from permissions@acm.org.
CCS’16, October 24-28, 2016, Vienna, Austria
c
2016 ACM. ISBN 978-1-4503-4139-4/16/10.. . $15.00
DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2976749.2978397
1. INTRODUCTION
Smartphones and tablets are commonly used for perform-
ing privacy sensitive transactions of banking, payment, and
social applications. Unlike stationary devices connecting to
a secure network and sitting in a physically-secure space,
these mobile devices are often carried by a mobile user and
connected to a dynamic network environment where attack-
ers can physically approach the target user’s device and
launch various direct and indirect eavesdropping attacks.
While direct eavesdropping attacks aim at directly observ-
ing the input of the target device from screen and keyboard,
indirect eavesdropping attacks, a.k.a. side-channel attacks
make use of side channels to infer the inputs on the target
devices. Prior works [2, 3, 12, 13, 15, 16, 18, 23, 25] have
shown that both types of attacks can be effective in cer-
tain situations. Particularly for the side-channel attacks, it
is shown that the PIN and the words entered at keyboard
can be inferred from the acoustic signal at microphone [3,
12, 25], electromagnetic signal at radio antenna [2], visible
light at camera [18, 23], and motion status at motion sensors
[13, 15, 16]. To access the side channels, these works often
assume either external signal collector devices are close to
the target device (for example, 30 cm) or the sensors of the
target devices are compromised to provide side channel in-
formation. However, in a mobile scenario, either assumption
is hardly true and the impact of attacks is thus limited. In
addition, the prior works [2, 3, 12, 13, 15, 16, 18, 23, 25]
have studied the keystroke inference aiming at achieving a
high inference accuracy on a series of keystrokes during a
relatively-long period of time. However, the keystrokes on
a mobile device are not always highly sensitive. Obviously,
the eavesdropping attacker has a greater interest in obtain-
ing the payment PIN number in a short moment than a
regular typing. Therefore, the application context informa-
tion also needs to be considered in the keystroke inference
framework. We will show how to use application context to
increase the inference effectiveness.
We present WindTalker, a novel and practical keystroke
inference framework that allows an attacker to infer the sen-
sitive keystrokes on a mobile device through WiFi signals.
WindTalker is motivated from the observation that the typ-
ing activity on mobile devices involves hand and the fin-
ger motions, which produce a recognizable interference to
the multi-path WiFi signals from the target device to the
WiFi router that connects to the device. Unlike prior side-
channel attacks or traditional CSI based gesture recognition,
WindTalker neither deploys external devices close to the tar-
1068
get device nor compromises any part of the target device;
instead, WindTalker setups a ‘rogue’ hotspot to lure the
target user with free WiFi service, which is easy-to-deploy
and difficult-to-detect. As long as the target device is con-
nected to the hotspot, WindTalker at the hotspot intercepts
the traffic and time-adaptively collect the channel state in-
formation (CSI) between the target device and the hotspot.
The design of WindTalker faces three major technical chal-
lenges. i) The impact of the hand and finger movement of
keystrokes on CSI waveforms is very subtle. An effective
signal analysis method is needed to analyze keystrokes from
the limited CSI. ii) The prior CSI collection method requires
two WiFi devices, one as a signal sender and the other as
a signal receiver, which are deployed close to the victim. A
more flexible and practical CSI collection method is highly
desirable for the mobile device scenario. iii) The key infer-
ence must be done at some selective moments for obtaining
a sensitive keystroke, such as payment PIN number. Such
context-oriented CSI collection has not been addressed by
prior works. In this paper, We introduce a novel CSI based
keystroke inference framework, which consists of four specif-
ical contributions.
• We present a practical CSI collection method using
public WiFi architecture without compromising the
victim’s device or deploying an external device very
close to the victim’s device. The victim’s device is
connected to a WiFi hotspot that stealthily collects the
CSI from the victim’s device by enforcing the ICMP
protocol. We further adopt the directional antenna
to eliminate CSI noises introduced by other factors in
public places, such as other people’s movement.
• We propose a keystroke recognition algorithm based
on the collected CSI. Specifically, we adopt low pass
filter to remove the high frequency noises and we use
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to reduce the
dimensionality of the feature vectors.
• We propose a context-oriented CSI collection method,
which employs both of the traffic analysis towards meta
data in WiFi traffic and CSI data analysis to recognize
the PIN input moment based on certain CSI tags. The
proposed method can be used to successfully figure out
the time of the PIN entry on Alipay (a popular mobile
payment platform in China) and launch the keystroke
recognition accordingly.
• We perform an extensive evaluation on keystroke in-
ference towards PIN input at the mobile payment pro-
cess, which is secured by the HTTPS protocol and thus
traditionally believed to be secure. Through our eval-
uation, we demonstrate that the attacker can infer the
PIN number at a high successful rate.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to
launch the keystroke inference towards PIN entry at the
mobile payment (e.g., Alipay). The remainder of this pa-
per is organized as follows. In Section 2, we introduce the
background of this work. In Section 3, we introduce the
research motivation by showing the correlation of keystroke
and CSI changing. We present the detailed design in Section
4, which is followed by Evaluation, Real-world experiment,
Discussion and Related work in Section 5, 6, 7 and 8, re-
spectively. Finally, we give the conclusion and future work
in Section 9.
RX
T
X
Smart device
Attacker
(a) IKI Model
T
X
RX
WiFi Router
Keyboard
Attacker
(b) OKI Model
Figure 1: WiFi-based Keystroke Inference Models
2. BACKGROUND
In this section, we introduce the scenario, the overview of
the keystroke inference methods, and preliminaries of chan-
nel state information.
2.1 Scenario
We consider a scenario where a user has a mobile device,
such as a smartphone, or a tablet and he or she is using
the public free WiFi through the device. It is a very com-
mon situation that people could have in the shopping mall,
the airport, and restaurants. A WiFi hotspot is set up at a
corner or on the ceiling, an unnoticeable location from the
user’s view. The user searches all the available WiFi sig-
nals at her device, and may choose to use the WiFi network
if the name of the network “looks” good and the network
is authentication-free. With the application layer security
(HTTPs), the user may believe that the Internet traffic is
protected from end-to-end such that the content shown at
the device and the user’s inputs at the device will be only
available to herself and the service provider. However, as
we will show, our WindTalker framework suggests effective
keystroke inference methods targeting at the mobile device.
2.2 In-band keystroke inference model
WindTalker chooses In-band keystroke inference (IKI) model.
As shown in Fig.1(a), WindTalker deploys one Commercial
Off-The-Shelf (COTS) WiFi device close to the target de-
vice, which could be a WiFi hotspot. The WiFi hotspot
provides free WiFi networks for nearby users. When a user
connects her device to the hotspot, the WiFi hotspot is able
to monitor the application context by checking the pattern
of the transmitted packets. In addition, the WiFi hotspot
periodically sends ICMP packets to obtain the CSI infor-
mation from the target device. With the meta data of the
WiFi traffic, the hotspot knows when the sensitive opera-
tions happen. And then, the hotspot adaptively launches
CSI-based keystroke inference method to recognize sensitive
key inputs. To the best of our knowledge, the IKI method we
propose is the first one using existing network protocols of
IEEE 802.11n/ac standard to obtain the application context
and the CSI information at mobile devices.
Note that the existing works about CSI based gesture
recognition choose another strategy: Out-of-band keystroke
inference (OKI) model[2]. In this model, the adversary de-
ploys two COTS WiFi devices close to the target device and
makes sure the target device is placed right between two
COTS WiFi devices. One is the sender device continuously
emitting signals and the other one is the receiver device con-
tinuously receiving the signals. The keystrokes are inferred
from the multi-path distortions in signals.
Compared with OKI model, the proposed IKI model has
the below advantages. Firstly, compared with OKI model,
1069
IKI model does not require the placement of both sender
andreceicerdeviceandcanbedeployedinamoreflexible
and stealthy way. Secondly, OKI model fails to differentiate
the non-sensitive operations on mobile devices (e.g., clicking
the screen to open an APP or just for web-browsing) from
sensitive operation (e.g., inputting the password). Instead,
IKImodelallowstheattackertoobtainbothofun-encrypted
meta data traffic as well as the CSI data to launch a more
fine-grained attack.
2.3 Channel State Information
The basic goal of WindTalker is measuring the impact of
hand and fingers’s movement on WiFi signals and leveraging
correlation of CSI and the unique hand motion to recognize
PIN. In the below, we briefly introduce the CSI related back-
grounds.
WiFi Standards like IEEE 802.11n/ac all support Multiple-
Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) and Orthogonal Frequency
Division Multiplexing (OFDM), which are expected to sig-
nificantly improve the channel capacity of the wireless sys-
tem. In a system with transmitter antenna number N
TX
,
receiver antenna number N
RX
and OFDM subcarriers num-
ber N
s
,systemwilluseN
TX
× N
RX
× N
s
subcarriers to
transmit signal at the same time.
CSI measures Channel Frequency Response (CFR) in dif-
ferent subcarriers f.CFRH (f, t) represents the state of
wireless channel in a signal transmission process. Let X (f,t)
and Y (f,t) represent the transmitted and received signal
with different subcarrier frequency. H (f,t)canbecalcu-
latedinreceiverusingaknowntransmittedsignalvia
H (f, t)=
Y (f,t)
X (f, t)
Since the received signal reflects the constructive and de-
structive interference of several multi-path signals scattered
from the wall and surrounding objects, the movements of
the fingers while password input can generate a unique pat-
tern in the time-series of CSI values, which can be used for
keystrokes recognition.
Many commercial devices such as Atheros 9390 [17], Atheros
9580 [22] and Intel 5300 [8] network interface cards (NICs)
with special drivers provide open access to CSI value. In
this study, we adopt Intel 5300 NICs, which follows IEEE
802.11n standard [1] and can work in 2.4GHz or 5GHz. By
selecting N
s
= 30 OFDM subcarriers, Intel 5300 NICs col-
lect CSI value for each TX-RX antenna pair.
3. MOTIVATION
In this section, we illustrate the rationale behind CSI
based keystroke inference on smart phones using real-world
experiments. Fig.2(a) shows the sketch of typical touching
screen during the PIN entry for mobile payment (e.g., Alipay
or Wechat pay). We particularly focus on the vertical touch
and the oblique touch, which are two most common touching
gestures [4, 7, 20]. As shown in the left of Fig.2(b), oblique
touch is the most common typing gesture, which happens
when people press different keys. Vertical touch usually hap-
pens when the human continuously presses the same key,
(e.g., continuously pressing 1) in the right of Fig.2(b).
We further investigate how these two common typing ges-
tures influence CSI. Generally speaking, since CSI reflects
the constructive and destructive interference of several multi-
path signals, the change of multi-path propagation during
(a) Finger typing
X
Y
Z
X
Y
Z
(b) Click
X
Y
Z
X
Y
Z
(c) Coverage
Figure 2: Finger’s influence on CSI
2000 4000 6000
15
20
25
30
35
40
Sam
p
le
CSI Amplitude
Number 1
4 4.2 4.4
x 10
4
0
5
10
15
20
Sam
p
le
CSI Amplitude
Number 6
5.6 5.8 6 6.2
x 10
4
15
20
25
30
35
Sam
p
le
CSI Amplitude
Number 8
7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7
x 10
4
15
20
25
30
35
40
Sample
CSI Amplitude
Number 0
(a) Continuously Click in Different Keys
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
8
x 10
4
0
10
20
30
40
50
Sample
CSI Amplitude
(b) Continuously Click in the Same Key
Figure 3: CSI Change When Typing
the PIN entry can generate a unique pattern in the time-
series of CSI values, which can be used for keystrokes in-
ference. From our experiments, we found that two main
factors contributing to CSI changes are hand coverage and
the finger click.
Hand coverage and finger position on a smart phone
touchscreen are one of the major factors that cause the fluc-
tuation of CSI waveform. It is widely acceptable that finger
position and coverage have a direct impact on the calling
quality. Similarly, since time series of CSI waveform reflects
the interference of several multi-path signals, different finger
position and coverage will inevitably introduce the interfer-
ence to the WiFi signals and thus lead to the changes of
the CSI. We further demonstrate the it via a series of ex-
periments. Fig.3(b) shows a CSI stream when continuously
pressing different number from 1 to 9, followed by 0, each for
5 times. It can be seen that the different coverages lead to
the different fluctuation range of the CSI value, which can
be exploited for key inference.
Finger click is another important factor that contributes
to the fluctuation of CSI. Compared with CSI change caused
1070
by the hand coverage, the experiment shows that finger click
has a more direct influence on CSI by introducing a sharp
convex in Fig.3(a), which corresponds to the quick click’s
influence on multi-path propagation. This feature can be
used to distinguish the oblique touches in the case that the
human continuously presses the same key or the adjacent
keys, which produce similar CSI values.
4. THE DESIGN OF WINDTALKER
4.1 System Overview
The basic strategy of WindTalker is hitting two birds with
one stone. On one hand, it analyzes the WiFi traffic to
identify the sensitive attack windows (e.g., PIN number) on
smartphones. On the other hand, as long as an attack win-
dow is identified, WindTalker starts to launch the CSI based
keystroke recognition. As shown in Fig.4, WindTalker is
consisted of the following modules: Sensitive Input Window
Recognition Module, which is responsible for distinguishing
the sensitive input time windows, ICMP Based CSI Acquire-
ment Module, which collects the user’s CSI data during his
access to WiFi hotspot, Data Preprocessing Module,which
preprocesses the CSI data to remove the noises and reduce
the dimension, Keystroke Extraction Module, which enables
WindTalker to automatically determine the start and the
end point of keystroke waveform, and Keystroke Inference
Module, which compares the different keystroke waveforms
and determines the corresponding keystroke.
Connected
Victim
Sensitive
Input
Directional
Antenna
Internet Control
Message
Protocol
CSI
Noise
Removal
Dimension
Reduction
Keystroke
Extraction
Keystroke
Recognition
Output
WiFi Packets
Analysis
Figure 4: WindTalker Framework
4.2 Sensitive Input Window Recognition Mod-
ule
To distinguish the time window of the sensitive input from
that of insensitive input, WindTalker captures all the pack-
ets of the victim with Wireshark and records timestamp of
each CSI data. Currently, most of the important applica-
tions are secured via HTTPS, which provides end-to-end
encryption and prevents the eavesdropper from obtaining
the sensitive data such as the password. Our insight is that
though HTTPS provides end-to-end encryption, it cannot
protect the meta data of the traffic such as the IP address
of the destination sever, which can be used to recognize sen-
sitive input window.
In particular, WindTalker builds a Sensitive IP Pool for
the interested applications or services. Take the AliPay as
an example. During the payment process, it will be directed
to a limited number of IP addresses, which can be obtained
via a series of trials. In the experimental evaluation, it is
shown that, for Alipay users, the traffics of the users under
thesamenetworkwillbedirectedtothesameserverIP,
which will last for a period (e.g., several days for one round
of experiment). This allows WindTalker to figure out the
sensitive input time window.
During the attack process, as long as the traffic to the
Sensitive IP Pool is observed, WindTalker will record the
corresponding start time and the end time, which serve as
the start and the end of the Sensitive Input Window. Then,
it starts to analyze the CSI data in this period to launch the
password inference attack via WiFi signals.
4.3 ICMP based CSI Acquirement Module
4.3.1 Collecting CSI Data by Enforcing ICMP Reply
Different from the previous works which rely on two de-
vices including both of the sender and the receiver to collect
CSI data, we apply an approach that leverages Internet Con-
trol Message Protocol (ICMP) in hotspot to collect CSI data
during the user accesses to the pre-installed access point. In
particular, WindTalker periodically sends a ICMP Echo Re-
quest to the victim smartphone, which will reply an Echo
Reply for each request. To acquire enough CSI informa-
tion of the victim, WindTalker needs to send ICMP Echo
Request at a high frequency, which enforces the victim to
replay at the same frequency. In practice, WindTalker can
work well for several smartphones such as XiaoMi, Samsung
and Nexus at the rate of 800 packets per second. It is im-
portant to point out that this approach does not require
any permission of the target smartphone and is difficult to
be detected by the victim.
ICMP based CSI collection approach introduces a limited
number of extra traffic. For a 98 bytes ICMP packet, when
we are sending 800 ICMP packets per second to the victim,
it needs only 78.4 kB/s for the attack where 802.11n can
theoretically support the transmission speed up to 140 Mbits
per second. It is clear that the proposed attack makes little
interference to the WiFi experience of the victim.
4.3.2 Reducing Noise via Directional Antenna
CSI will be influenced by both finger movement and peo-
ple’s body movement. One of the major challenges of ob-
taining the exact CSI data in public space is how to min-
imize the interference caused by the nearby human beings.
We present a noise reduction approach by adopting the di-
rectional antenna. Different from omni-directional antennas
that have a uniform gain in each direction, directional an-
tennas have a different antenna gain in each direction. As a
result the signal level at a receiver can be increased or de-
creased simply by rotating the orientation of the directional
antenna. WindTalker employs directional antenna to focus
the energy toward the target of interest, which is expected to
minimize the effects of the nearby human body movement.
WindTalker employs a TDJ-2400BKC antenna working
in 2.4GHz to collect CSI data of the targeted victim, whose
Horizontal Plane -3dB Power Beamwidth and Vertical Plane
-3dB Power Beamwidth are 30
◦
and 25
◦
respectively. Con-
sidering the case that the distance between the victim and
access point is 1.5 meter, we illustrate the effective accep-
tance area of 0.67 meter high and 0.80 meter long.
Fig.5 shows the comparison of CSI collection with direc-
tional antenna and without directional antenna in public
place. Fig.5(b), Fig.5(c), Fig.5(d) show CSI amplitude in
1071
0 2000 4000 6000
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
Sample
CSI Amplitude
(a) Omni-directional An-
tenna in 75cm
0 2000 4000
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
Sample
CSI Amplitude
(b) Directional Antenna
in 75cm
0 2000 4000 6000
18
20
22
24
26
28
Sample
CSI Amplitude
(c) Directional Antenna
in 125cm
0 2000 4000 6000
16
18
20
22
24
Sample
CSI Amplitude
(d) Directional Antenna
in 150cm
Figure 5: Antenna Performance in Public Place
the case that a victim is located at 75, 125, 150 cm accord-
ingly away from directional antenna while one people moving
nearby. Unique pattern caused by finger click in number 1
can be easily caught from the original CSI stream without
any preprocessing. However, these patterns are submerged
in human body’s influence on CSI stream obtained by omni-
directional antenna even when the victim and attacker is
close as 75 cm, which is shown in Fig.5(a).
4.4 Data Preprocessing Module
Before launching keystroke inference module, WindTalker
needs to preprocess the CSI data to remove the noises intro-
duced by commodity WiFi NICs due to the frequent changes
in internal CSI reference levels, transmit power levels, and
transmission rates. To achieve this, WindTalker first turns
to low pass filter to remove the high frequency noise. Then,
WindTalker leverages the Principal Component Analysis to
reduce the dimensionality of the feature vectors to enable
better analysis of the data.
4.4.1 Low Pass Filtering
The observation behind low pass filtering is that the vari-
ations of CSI waveforms caused by finger motion lie at the
low end of the spectrum while the frequency of the noise lies
at the high end of the spectrum. To remove noise, we adopt
Butterworth low-pass filter, which is designed to have a flat
frequency response in the passband and thus does not distort
the finger motion signal much. It is observed that the fre-
quencies of the variations in CSI time series due to hand and
finger movements lie between 2 Hz and 30 Hz. As we sample
CSI values at a rate of S = 800 packets/s, WindTalker sets
some parameters to choose a proper filter in which the tran-
sition band ranges from 30Hz to 80Hz. We set the passband
corner frequency W
p
=
2∗f
p
S
=
2∗30
800
≈ 0.075 πrads/sample
with 1 corresponding to the normalized Nyquist frequency
and stopband corner frequency W
s
=
2∗f
s
S
=
2∗80
800
≈ 0.2
πrads/sample. Passband ripple in decibels is 1 and Stop-
band attenuation in decibels is 40. After low-pass filter,
most of the burst noises can be removed.
4.4.2 Dimension Reduction
Dimension reduction is essential for keystroke inference
via CSI information. For a CSI recording system using In-
tel 5300 NICs with N
TX
transmitter antennas and N
RX
re-
ceiver antennas, it can collect N
TX
×N
RX
×30 CSI streams.
It is important to reduce the dimensionality of the CSI infor-
mation obtained from 30 subcarriers in each TX-RX stream
and recognize those subcarriers which show the strongest
correlation with the hand and finger movements. WindTalker
adopts PCA, which is expected to choose the most repre-
sentative or principal components from all CSI time series.
PCA is also expected to remove the uncorrelated noisy com-
ponents. The procedure of dimension reduction of CSI time
series based on PCA includes the following steps.
Sample Centralization: Performing sample centraliza-
tion in every subcarries. We use a matrix H to present orig-
inalCSIstreamdata. Forexample,inasystemwithone
pair of TX-RX antenna, we will get 30 CSI streams from 30
subcarriers. Thus, with sample rate S and time T , H has
dimension of M × 30, where M = S × T .Everycolumn
of H represents a CSI time series data stream in one sub-
carrier. Then we calculate the mean value of each column
in H and subtract the corresponding mean values in every
column. After the centralization step, we get a processed
matrix H
p
.
Calculating Covariance Matrix: Calculating the cor-
relation matrix of H
p
as H
p
T
× H
p
.
Calculating Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of Co-
variance: Calculating the Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of
Covariance. The Eigenvectors are normalized to unit vec-
tors.
Choosing Main Eigenvalues: Sorting the Eigenvalues
from large to small and choosing the maximum k number
of Eigenvalues. Then the corresponding k Eigenvectors are
used as the column vectors to form a Eigenvector matrix.
We will get a Eigenvector matrix whose dimension is 30×k.
Data Reconstruction: Projecting H
p
onto the selected
k Eigenvector matrix. The reconstruction CSI data stream
H
r
has the dimension of M × k.
H
r
(M × k)=H
p
(M × 30) × EigenV ectors(30 × k)
With PCA, we can identify the most representative com-
ponents influenced by the victim’s hand and finger’s move-
ment and remove the noisy components at the same time.
In our experiment, it is observed the first k =4components
almost show the most significant changes in CSI streams
and the rest components are noises. We only take one PCA
component from the first 4 components in the password in-
ference module. We observed that the first PCA compo-
nent reserves most changes in CSI while the ambient noise
is weakly. Otherwise, the first component has a large noise
and the succeeding k − 1 components reserve most changes
in CSI.
4.5 Keystroke Inference Module
4.5.1 Keystroke Extraction
By processing the low pass filtering and dimension reduc-
tion, it is observed that the CSI data shows a strong corre-
lation with the keystrokes. In the experiment, the sharp rise
1072
0 2000 400 0 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000
-1
0
1
2
3
Sam
p
le
CSI Value
(a) After Once Filter
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000
-1
0
1
2
3
Sample
CSI Value
(b) After Twice Filter
1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7
x 10
4
−0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
Sample
CSI Value
J Anchor Points
(c) Judgement Value
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000
-1
0
1
2
3
Sample
CSI Value
CSI Value
Variance
(d) Variance Scan
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000
-1
0
1
2
3
Sample
CSI Value
CSI Value
Start Point
End Point
(e) The Results of Extraction
1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7
x 10
4
−0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
Sample
CSI Value
J
Start Point
End Point
(f) Keystroke Area
Figure 6: Keystroke Extraction
andfalloftheCSIwaveformsignalsareobservedincoinci-
dence with the start and end of finger touch. How to deter-
mine the start and the end point of CSI time series during a
keystroke is essential for keystroke recognition. However, the
existing burst detection schemes such as Mann-Kendall test
[9], moving average method [10] and cumulative anomalies
[14] do not work well in our situation since the CSI waveform
has many change-points during the password input period.
Therefore, we propose a novel detection algorithm to au-
tomatically detect the start and end point. The proposed
algorithm includes the following three steps.
Waveform Profile Building: AsshowninFig.6(a),itis
observed that there is a sharp rise and fall which correspond
to the finger motions. However, there is a strong noise which
prevents us from extracting interested CSI waveform related
to the keystrokes. This motives us to perform another round
of noise filtering. In the experiment, we adopt Butterworth
filter and choose 10Hz as the cutoff frequency to make the
waveform smooth. After being filtered, the CSI data during
the keystroke period are highlighted while the waveform dur-
ing non-keystroke period becomes smooth, which are shown
in Fig.6(b).
CSI Time Series Segmentation and Feature Seg-
ment Selection: To extract the CSI waveforms for indi-
vidual keystrokes, we slice the CSI time series into multiple
segments, which be grouped together according to the tem-
poral proximity, and then choose the center of segment as
the feature waveform for a specific keystroke. Without loss
of the generality, it is assumed that each segment contains
W samples. Given the sampling frequency S, and the time
duration τ , W can be represented by S × τ.Forthewave-
form with time duration of T , the number of segments N
can be calculated as below:
N =
T × S
W
It is observed that the CSI segments during the keystroke
period show a much larger variance than those happening
out of the period, which is shown in Fig.6(d). Motivated by
this, we are only interested in the segments with the vari-
ance which is larger than a predetermined threshold while
removing the segments with the variance under this thresh-
old. The selected segments are grouped into various groups
according to the temporal proximity (e.g., five adjacent seg-
ments grouped into one group in the practice). Each group
represents the CSI waveform of an individual keystroke and
the center point of this group is selected as the feature seg-
ment of this keystroke. The process of time series segmen-
tation and feature segment selection is shown in Fig.6(d).
Keystroke Waveforms Extraction: To extract keystroke
waveforms, the key issues is how to determine the start and
the end point of CSI time series, which could cover as much
keystroke waveform as possible while minimizing the cov-
erage of the non-keystroke portion. We choose the average
value of the segment samples J as the key metric and the
intersection of J and the CSI waveform serves as the an-
chor points. In particular, starting from the leftmost anchor
point, it performs a local search and chooses the nearest lo-
cal extremum which is below J as the start point. Similarly,
beyond the rightmost anchor point, it can choose the near-
est local extremum which is below J as the end point. As
shown in Fig.6(c), Fig.6(f), Fig.6(e), with the start and the
end point, keystroke waveform can be extracted.
Thus, we can divide a CSI stream into several keystroke
waveform. The i
th
keystroke waveform K
i
from the k
th
principal component H
r
(:,k) of CSI waveforms as follows.
K
i
= H
r
(s
i
: e
i
,k)
where s
i
and e
i
be the start and the end time of i
th
keystroke.
After keystroke extraction, we use these keystroke waveform
to conduct recognition process.
4.5.2 Keystroke recognition
One of the major challenges for differentiating keystrokes
is how to choose the appropriate features that can uniquely
represent the keystrokes. As shown in Fig.7, it is observed
that different keystrokes will lead to different waveforms,
which motivates us to choose waveform shape as the feature
for keystroke classification. To compare the waveforms of
different keystrokes, we adopt the Dynamic Time Warping
(DTW) to measure the similarity between the CSI time se-
ries of two keystrokes. However, directly using the keystroke
1073
0 500 1000 1500 2000
−10
0
10
20
Sample Index
CSI Value
0 500 1000 1500
−5
0
5
10
15
Sample Index
CSI Value
(a) Two samples of keystroke waveforms number 2
0 500 1000 1500
−15
−10
−5
0
5
Sample Index
CSI Value
0 500 1000 1500 2000
−10
−5
0
5
10
Sample Index
CSI Value
(b) Two samples of keystroke waveforms number 4
Figure 7: CSI Difference Between Two Number
waveforms as the classification features leads to high com-
putational costs in the classification process since waveforms
contain many data points for each keystroke. Therefore, we
leverage Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to compress
the length of CSI waveform by extracting the approximate
sequence. In the below, we will introduce the details.
4.5.3 Discrete Wavelet Transform
Different from the traditional frequency analysis such as
Fourier Transform, DWT is the time-frequency analysis which
has a good resolution at both of the time and frequency do-
mains. A discrete signal x [n] can be expressed in terms of
the wavelet function by the following equation:
x[n]=
1
√
L
k
W
φ
[j
0
,k]φ
j
0
,k
[n]+
1
√
L
∞
j=j
0
k
W
ψ
[j, k]ψ
j,k
[n],
where x[n] represents the original discrete signal and L
represents the length of x[n]. φ
j
0
,k
[n]andψ
j,k
[n]referto
wavelet basis. W
φ
[j
0
,k]andW
ψ
[j, k] refer to the wavelet
coefficients. The functions φ
j
0
,k
[n] refer to scaling functions
and the corresponding coefficients W
φ
[j
0
,k] refer to the ap-
proximation coefficients. Similarly, functions ψ
j,k
[n] refer
to wavelet functions and coefficients W
ψ
[j, k] refer to detail
coefficients. To obtain the wavelet coefficients, the wavelet
basis φ
j
0
,k
[n]andψ
j,k
[n] are chosen to be orthogonal to each
other.
During the decomposition process, the origin signal is first
divided into the approximation coefficients and detail coef-
ficients. Then the approximation coefficients are iteratively
divided into the approximation and detail coefficients of next
level. The approximation and the detail coefficients in j
th
level can be calculated as follows:
W
φ
[j
0
,k]=x[n],φ
j
0
+1,k
[n] =
1
√
L
n
x[n]φ
j
0
+1,k
[n]
W
ψ
[j, k]=x[n],ψ
j+1,k
[n] =
1
√
L
n
x[n]ψ
j+1,k
[n]
In the first DWT decomposition step, the length of ap-
proximation coefficients is half of L.Forthej
th
decompo-
sition step, the length is half of the previous decomposition.
We use the approximation coefficients to compress the orig-
inal keystroke waveforms to reduce computational cost. In
order to achieve the tradeoff between the sequence length
reducing and preserving the waveform information, we need
to choose an appropriate wavelet basis and decomposition
level. In practice, we choose Daubechies D4 wavelet and per-
form 3-level DWT decomposition in the classification model.
Therefore, for i
th
keystroke, the third level approximation
coefficients of K
i
is chosen as the feature of the keystroke.
4.5.4 Dynamic Time Warping
To compare features of different keystrokes, WindTalker
adopts DTW to achieve keystroke recognition. DTW utilizes
dynamic programming to calculate the distance between two
time series of keystroke waveforms with different lengths.
With DTW, the sequences (e.g., time series) are warped non-
linearly in the time dimension to measure their similarity.
The input of DTW algorithm is two time series and the
output is the distance between two series. A low distance
indicates that these two sequences are highly similar.
4.5.5 Classifier Training
We build a classifier to recognize the keystrokes based
on their keystroke waveform shapes. Our classifier gives
each keystroke waveform a set of scores, which allows the
keystrokes to be differentiated based on the user’s training
dataset (keystrokes on different numbers). For a certain
key number, classifier first calculates the DTW distances
between the input waveform and all the key number’s wave-
forms in dataset. Then classifier chooses the average value of
the previous distances as the score between the input wave-
form and the certain key number. The smaller the score, the
higher possibility the certain number is actual input num-
ber. The classifier choose the key number which has the
minimum score as the predicted key number. Note that the
classifier saves all scores in order to generate password can-
didates in Section 5.3.
5. EVALUATION
5.1 System Setup
WindTalker is built with the off-the-shelf hardware, which
is actually a commercial laptop computer equipped with In-
tel 5300 NIC with one external directional antenna and two
omni-directional antennas. WindTalker also serves as the
WiFi hotspot to attract the users to access to the WiFi. The
laptop runs Ubuntu 14.04 LTS with a modified Intel driver
to collect CSI data. To collect the CSI data related to the
user’s touch screen clicks, WindTalker uses ICMP echo and
reply to achieve the sampling rate of 800 packets/s. In this
evaluation, the distance between the mobile user and the
AP is 75 cm and the AP is placed on the left side of mobile
phone.
In the online phase, we recruit 10 volunteers to join our
evaluation, including 7 males and 3 females. All of the vol-
unteers are right-handed and they perform the touch-screen
operations by following their own fashions. During the ex-
periment, the volunteers should participate in the data train-
ing phase and keystroke recognition phase by inputting the
numbers according to the system hints. In the data training
phase, WindTalker records each input and its corresponding
CSI data. In the test phase, WindTalker infers the input
data based on the observed CSI time series. The training
data and testing data collection should be finished within 30
1074
Figure 8: Classification Accuracy per key
minutes since CSI may change with the change of environ-
ment.
We start the evaluation by testing the classification accu-
racy and the 6-digit password inference accuracy. Then we
investigate various metrics that may influence the inference
accuracy of WindTalker including the distance and the di-
rection. Afterwards we perform a more specific case study
by inferring the password of mobile payment for Alipay in
Section 6. In the current stage evaluation, we only perform
user specific training and will discuss it’s limitation in Sec-
tion 7.
5.2 Classification Accuracy
In Section 3, we have shown that different keystrokes may
be correlated with different CSI waveforms. In this section,
we aim to explore whether the differences of keystroke wave-
forms are large enough to be used for recognizing different
keys inputs in the real-world setting. We collected training
and testing data from 10 volunteers. Each volunteer first
generates 10 loop samples, where a loop is defined as the
CSI waveform for key number from 0 to 9 by pressing the
corresponding digit. After that, we evaluate the classifica-
tion accuracy of WindTalker through the collected CSI data.
The classification accuracy is evaluated in terms of cross val-
idation accuracy. In our problem setting, for every 10 loops
dataset, we pick up one loop in turn for the testing data and
choose the other 9 loops as the training dataset. WindTalker
adopts the classifier introduced in Section 4.5 to recognize
the keystroke. We perform the evaluation on Samsung Note
5 , Xiaomi Redmi Note 3 and Nexus 5. These mobile are run
with Android 6.0.1, 5.0.2 and 6.0.1, respectively. When we
use all ten loops data, WindTalker achieves average accuracy
classification of 81.8% in Xiaomi, 73.2% in Nexus and 64%
in Samsung. Fig.8 shows average classification accuracy of
all 10 volunteers in 10 PIN number.
Fig.9 describes the color map of confusion matrix of Xi-
aomi. For a specific typed number, it gives the correspond-
ing inference results. The darker the area is, the higher the
possibility of keystroke inference result is. Intuitively, it is
easier for an input number that is confused with the neigh-
boring numbers during the keystroke inference process.
5.3 Password Inference
In a practical scenario setting, it may not be easy for
WindTalker to get 10 training samples for each PIN num-
ber. So in the remaining section, we only use 3 samples
per number for training. To illustrate the performance of
WindTalker for password Inference, in this part, we ask vol-
unteers to press 10 randomly generated 6-digit passwords
Predicted Key Number
Actual Key Number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
Figure 9: Color Map
Table 1: Recovery Rate and Candidates Number
Phone One Two Three
SamSung 0.63 0.83 0.89
XiaoM i 0.79 0.88 0.95
and use their corresponding 3 loops as training dataset. This
experiment is repeated in both Samsung and XiaoMi.
We test totally 200 set of passwords, which include 1200
keys. The inference results show that totally 852 keys were
recovered. As shown in Table.1, WindTalker can achieve an
average 1-digit recovery rate of 79.0% in XiaoMi and 63.0%
in SamSung. For a 6-digit password in AliPay, the attacker
can try several times to recover the password at an increased
successful rate. Thus, we introduce a new metric, recov-
ery rate with Top N candidates, which indicates the rate of
successfully recovering the password for trying N times and
represents a more reasonable metric to describe the capa-
bility of the attacker in the practical setting. As shown in
Table.1, if we evaluate the 1-digit recovery rate under top 2
and top 3 candidates, it is found that the recovery rate can
be significantly improved.
We further study how many candidates can help us to
succeed in predicting the right 6-digit payment password in
WindTalker. In particular, we will investigate the inference
accuracy under top N candidates. In the experiment, each
6-digit password will be correlated with six CSI waveforms.
For each waveform, WindTalker calculates the probability
of matching the waveform with the predict key number.
The probability of a predicted password is defined by the
product of the six probabilities. For a 6-digit password, we
can obtain 100000 predicted password, then sort these pass-
word by their probabilities in descending order. A success-
ful password inference is defined as that the real password
0 5 10 15 20
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Number of candid ate passwords
Password Inference Accuracy (%)
(a) Top 20 Candidates
20 40 60 80 100
50
60
70
80
90
Number of candidate
p
asswords
Password Inference Accuracy (%)
(b) Top 100 Candidates
Figure 10: 6-digit Password Inference Accuracy
1075
(a) Distance
0 50 100
−20
−10
0
10
20
30
Temporal Units
Approximation Coefficients
75 cm
0 50 100
−10
0
10
20
Temporal Units
Approximation Coefficients
100 cm
0 50 100
−20
−10
0
10
20
30
Temporal Units
Approximation Coefficients
125 cm
0 100 200
−30
−20
−10
0
10
20
30
Temporal Units
Approximation Coefficients
150 cm
PCA 2nd Component PCA 3rd Component PCA 4th Component
(b) CSI Shape Change by Distance
Figure 11: Distance’s influence in WindTalker
is included in top N candidates. In Fig.10(a) ,we give the
password inference accuracy under top N candidates, where
N ranges from 1 to 20. The result is encouraging. It is
shown that, given top 1 candidate, the inference accuracy is
only 20%. The inference rate can be significantly improved
if given top 5 candidates or top 10 candidates, which corre-
spond to 38% and 42%, respectively. It is also shown in Fig.
10(b) that, if given enough top N candidates (e.g., set N as
85), the inference accuracy can reach almost 80%.
5.4 Impact of Distance and Direction
There are many factors potentially impacting the CSI.
Even clicking at the same key, the different distance and
direction between AP and the mobile device may also lead
to a quite different CSI. We will investigate the impact of
the distance and the direction on CSI in our experiments.
5.4.1 Distance
In a real scenario, the distance between victim’s mobile
device and AP is not fixed. As shown in Fig.11(a), the
recovery rate of WindTalker will decrease along with the in-
crease of the distance. However, it is observed that, even
if the distance is enlarged to 1.6m, WindTalker can still
achieve 1-digit recovery rate 70% under top 3 candidates. It
demonstrates that WindTalker can work well even if the dis-
tance reaches 1.6m. This is because with WindTalker, the
attacker can enforce the smart phones to send WiFi signals
and AP to receive the WiFi signals. In this setting, though
the distance between the victim and receiver (AP) is en-
Figure 12: Accuracy in Different Direction
larged, the distance between the WiFi sender (smart phone)
and the victim (fingers) is relatively stable, which guaran-
tees key recognizing. Fig.12 shows that both CSI shape and
degree will change under different distance. This indicates
that WindTalker needs to retrain dataset even for the same
victim with different distances. To partially solve this limi-
tation, in practice, the attacker can fix the location of table
and chairs, which will make the user’s position relatively
stable.
5.4.2 Direction
The relative direction between the victim and attacker
may seriously affect the CSI since different directions mean
different multi-path propagation between the transmitter
and the receiver. Thus, we show the performance of WindTalker
under different directions. Note that the mobile device is in
front of victim in experiments. It is important to point out
that, for a right-handed user, WindTalker shows a better
performance when the AP is on the left side of the victim.
This is because it is easier for WindTalker to sense victim’s
finger clicks and the hand motion. Fig.12 shows the recovery
accuracy of WindTalker in different direction. It is interest-
ing that WindTalker can achieve a high performance even
the AP is deployed behind victims, which means that the
proposed CSI based keystroke inference can work well even
if the attacker is behind the user without visually seeing the
clicking actions. This represents one of significant merits
which cannot be achieved by any previous work.
6. REAL-WORLD EXPERIMENT: MOBILE
PAYMENT PASSWORD INFERENCE TO-
WARDS ALIPAY
6.1 System Setup
To demonstrate the practicality of the WindTalker, we
perform an experimental evaluation of password inference on
Alipay, a popular mobile payment platform on Both of An-
droid and iOS system. Alipay is the largest mobile payments
company in the world and has 450 million monthly active
user including 270 million mobile payment users. As shown
in Fig.13, we deploy a WindTalker system at a cafeteria-like
environment and release an authentication-free WiFi. The
AP (including Intel 5300 NIC and the antennas) is set up
behind the counter, which makes it less likely to be detected
visually. The victim is 1 meter away from our deployed WiFi
devices. When we collect the data, one user walks pass by
the victim but none of users walks between the victim and
the AP.
To simulate the real-world attack scenarios, the recruited
volunteers are required to access to this free WiFi access
1076
Targe t
Hidden
Devices
Intel 5300 NIC
Antennas
1m
Figure 13: Real Case Scenario
points and perform the following three phases: 1) Online
Training Phase: the volunteers are required to input some
randomly generated numbers by following a similar way as
Text Captchas. This phase is designed to collect the user’s
input number and the corresponding CSI data to finish the
data training. 2) Normal Use Phase: the volunteers perform
the online browsing or use the applications as a normal user.
3) Mobile Payment Phase: when the users use the online
shopping applications, it will be ended with the mobile pay-
ment. All of the online shopping and mobile payments are
secured with HTTPS protocol. According to Alipay mobile
payment policy, the mobile users must input the password
to finish an mobile payment transactions. The goal of the
attacker is to recover the mobile payment password of the
volunteers.
6.2 Operations of WindTalker
After the volunteers connect to the authentication-free
WiFi hotspot, WindTalker triggers ICMP based CSI Ac-
quirement Module to collect the CSI data at the sampling
rate of 800 packets/s. WindTalker records the timestamp
per one hundred CSI data. Simultaneously, WindTalker
utilizes Wireshark to capture and record WiFi traffic pack-
ets and their corresponding timestamp. During the real-
world experiment, WindTalker collects WiFi traffic data and
CSI data in the online phase. After collecting the data,
WindTalker infers the user’s mobile payment password in
the offline phase.
6.3 Recognizing The Sensitive Input Windows:
To determine the sensitive input windows, WindTalker
runs in a real-time fashion to collect the meta data (e.g., IP
address) of the targeted sensitive mobile payment applica-
tions (e.g., Alipay). For example, in the experiment, Alipay
applications will always route their data to the server of
some specific IP address such as “110.75.xx.xx”. This IP
address will be kept to be relatively stable for one or two
weeks. With the traffic meta data, as shown in Fig.14(a),
WindTalker obtains the rough start time and end point of
Sensitive Input Window via searching packets whose desti-
nation is “110.75.xx.xx”. Then WindTalker begins to ana-
lyze the corresponding CSI data in that period of time.
6.4 CSI based Password Inference
Fig.14(b) shows the original 12th subcarrier CSI data in
Sensitive Input Window. After data preprocessing, Fig.14(c)
shows the first three principal components of CSI data af-
ter PCA. It is found that in the real-world experiment that
besides input payment password, victim may have other op-
erations such as selecting credit card for payment in period
Start
End
…
Time
Time
(a) Sensitive Input Windows Recog-
nition Module
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5
x 10
4
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
A CSI se
q
uence containin
g
a Sensitive :LQGRZ
CSI Amplitude
(b) Original CSI
Sensitive Input Window
Keystroke Extraction
Keystroke Inference
7
7
9
9
3
1
(c) Keystroke Inference Module
Figure 14: WindTalker in Case Study
of time of Sensitive Input. In order to handle this situation,
WindTalker only needs to find a continuous keystroke of cer-
tain length. In our case, we are interested in continuous 6-bit
password input since Alipay chooses 6-digit mobile payment
password. Thus after keystroke extraction and recognition
process, WindTalker is able to list possible password can-
didates according to probability. The top three password
candidates in this case is 773919, 773619, 773916 while the
actual password is 773919. We carry out the real-world ex-
periment ten times, each time the password is different. Our
experiment results show that the attacker can successfully
recover 2, 4, 7 and 9 passwords if allowing to try the pass-
word input for 5, 10, 50 and 100 times (or Top 5, 10, 50, and
100 candidates). This further demonstrates the practicality
of the proposed attack in the practical environment.
7. DISCUSSIONS
7.1 Limitations
In this section, we discuss the main limitations of WindTalker.
WindTalker’s high performance is achieved in an experiment
environment. However, if we try to apply WindTalker in
anytime and anyplace, we need to overcome the limitations
as follows.
Hardware Limitations. In WindTalker, we use Intel
5300 NIC and Linux 802.11n CSI Tool[8]. In our experi-
ments, it is observed that the system will crash when we
perform ICMP based CSI data collection for iPhone or some
version of android smart phones. This is because, according
to the statement of the author of CSI Tool, it is very easy to
crash when one Intel 5300 NIC works with other NICs (e.g.,
an iPhone). However, our implementation and evaluation
on a wide range of smart phones (including XiaoMi phones,
Nexus and Samsung phones) demonstrate the practicality
of the proposed CSI based keystroke inference method. We
will leave the issues of improving the compatibility of Intel
5300 NIC with a wider range of mobile devices to our future
work.
1077
Table 2: Recovery Rate and Loop Times
Loop Times One Three Five Ten
Recovery Rate 68.3% 73.3% 78.3% 81.7%
Fixed Typing Gesture. Currently, WindTalker can
only work for the situation that the victim can only touch
the screen with a relatively fixed gesture and the phone needs
to be placed in a relative stable environment (e.g., a table).
In reality, the user may type in an ad-hoc way (e.g., the vic-
tim may hold and shake the phone, or even perform some
other actions while typing). We argue that is a common
problem for most of the side channel based keystroke in-
ference schemes such as [2, 13, 16]. This problem can be
partially circumvented by profiling the victim ahead or per-
forming a targeted attack by applying the relevant move-
ment model as pointed out by [13].
User Specific Training. Using WindTalker, the vic-
tim’s input can be recognized via the classifiers trained from
the same user. In the real-world experiments, it is hard to
adopt the classifiers trained by other people to infer the vic-
tim’s input. This is because different people have different
finger coverage and clicking model. A large number of train-
ing data based on a wide range of training samples may over-
come this limitation. In practice, the attackers have more
choices to achieve the user specific training. For example, it
can simply offer the user free WiFi access and, as the return,
the victim should finish the online training by clicking the
designated numbers. It can also mimic a Text Captchas to
require the victim to input the chosen numbers. We further
analyze the impact of the number of training data on re-
covery rate in WindTalker. Table.2 shows the recovery rate
increases with the training loop increases. Even if there is
only one training sample for one keystroke, WindTalker can
still achieve whole recovery rate of 68.3%.
7.2 Defending Strategies
One of the most straightforward defense strategies is to
randomize the layouts of the PIN keypad, such that the
attacker cannot recover the typed PIN number even if he can
infer the keystroke positions on the touchscreen. As pointed
out by [23], randomizing the keyboards is the effective at the
cost of the user experience since the user needs to find every
key on a random keyboard layout for every key typing.
A more practical defense strategy is preventing the collec-
tion of CSI data. For example, the user refuses to connect
to free public WiFi or pays attention to the deployed WiFi
devices nearby. Note that, to have the successful CSI based
keystroke inference, the sender WiFi device should be de-
ployed close enough to the victim (e.g., 30 cm as shown in
[2]). To prevent the accurate CSI data collection, another
strategy is obfuscating the CSI data by adding some ran-
domized noises to CSI data. In particular, the user can
intentionally change his typing gestures or clicking patterns,
since finger coverage and click pattern are considered as two
major factors that affect CSI value for the keystroke. Fur-
ther, since CSI reflects the change of multi-path propagation
of WiFi signals, the users can take some actions to introduce
the unexpected interferences to the CSI data. For example,
the randomized human behaviors (e.g., human mobility) or
wireless signals will reduce the successful chance of the ad-
versary. Lastly, for the proposed ICMP based CSI collection
approach, CSI based typing inference requires collecting CSI
data with a high frequency. Therefore, detecting and pre-
venting a high-frequency ICMP ping represent a practical
and ease of use countermeasure.
8. RELATED WORK
In this section, we review two domains of prior works that
are tightly related to WindTalker.
8.1 Public free Wi-Fi with malicious behav-
iors
Free Wi-Fi services provided by public hotspots are at-
tractive to users in a mobile environment when their mobile
devices have limited Cellular connection. Existing works
[5, 6, 11, 21] have demonstrated it is feasible to deploy
a malicious Wi-Fi hotspot in a public area. For exam-
ple, an iPhone can turn itself into a Wi-Fi hotspot. If the
iPhone user changes the session ID to “Starbucks Free Wi-
Fi”, other people may connect their phones to the iPhone
while wrongly believe they are using free WiFi services from
a nearby Starbucks.
In our considered scenarios, attackers may make use of
user’s trusts on pubic WiFi and lure the the users to con-
nect their devices to a fake access point. Then, the attacker
eavesdrops the WiFi traffic to identify the sensitive win-
dows and selectively analyzes the CSI information to infer
the keystroke information.
8.2 Keystroke Inference methods
Prior keystroke inference methods have been developed
based on the information from various sensors and commu-
nication channels, such as motion, camera, acoustic signals,
and WiFi signals.
Motion: Owusu et al. [16] presented an accelerometer-
based keystroke inference method, which aims to recover
six-character passwords on smartphones. Later, Liu et al.
[13] applied a similar idea to the smartwatch scenario. Their
objective is to track user’s hand movement over the keyboard
using the accelerometer readings from the smartwatch, and
the keystroke inference achieves 65% recognition accuracy.
Acoustic signals: Zhu et al. [25] presented a context-
free and geometry-based keystroke inference. They use the
microphones at a smartphone to record keystrokes’ acoustic
emanations. Liu et al. [12] further proposed a keystroke
snooping system by exploiting the audio hardware to dis-
tinguish mm-level position difference. Their experiments
showed the system can recover 94% of keystrokes.
Camera based: Yue et al. [23] introduces a camera-
based keystroke inference using Google Glass or off-the-shelf
webcam. This method can achieve a per-input success rate
of over 90%. Shukla et al. [18] also presented a video-based
attack relies on the spatio-temporal dynamics of the hands
during typing. The paper can breaks an average of over
50% of the PINs. Sun et al. [19] use camera to record tablet
backside motion and infer the victim’s typing content.
WiFi signal based: Using Wi-Fi signals to infer the
keystroke recently draws a large research attention because
it offers device-free and non-invasion advantages. The chan-
nel state information (CSI) are obtained from the commer-
cial Wi-Fi network interface cards. Many research works
have demonstrated such fine-grained information can be very
effective in detecting the ambient physical movement be-
cause it well captures the reflected multi-path WiFi signals.
1078
Liu et al. [2] proposed a keystroke inference systems called
WiKey, which uses the CSI waveform pattern generated by
finger’s unique motion to distinguish keystrokes on a exter-
nal keyboard. Compared with our work, WiKey works on
the OKI keystroke inference model and it can not recognize
the sensitive input windows. Zhang et al. [24] also pre-
sented WiPass, which can work in mobile device to detect
the graphical unlock passwords.
9. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
In this paper, we have designed and evaluated a novel
side-channel attack based on CSI which can infer victim’s
input on smartphone via WiFi signals. Our evaluation shows
that our attack can work well in recognizing the victim’s
password on smart phones. Compared with the previous
side channel based keystroke inference work, WindTalker
neither deploys external devices close to the target device
nor compromises the target device. It can even be launched
behind the victim without the requirement of visually seeing
the smart phone user’s input process, backside motion, or
installing any malware on the tablet. Due to the limitation
of Intel 5300 NIC, the current WindTalker cannot work for
iOS smartphones, which will be a part of our future work.
We will investigate how to further improve the inference
accuracy of WindTalker under different environments.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Science Foundation of
China (No. 61272444, U1401253, U1405251, 61411146001)
and National Science Foundation (No. 1527144, No. 1553304,
No. 1618893).
10. REFERENCES
[1] IEEE Std. 802.11n-2009: Enhancements for higher
throughput. http://www.ieee802.org, 2009.
[2] Ali, K., Liu, A. X., Wang, W., and Shahzad, M.
Keystroke recognition using wifi signals. In Proceedings of
the 21st Annual International Conference on Mobile
Computing and Networking (2015), ACM, pp. 90–102.
[3] Balzarotti, D., Cova, M., and Vigna, G. Clearshot:
Eavesdropping on keyboard input from video. In Security
and Privacy, 2008. SP 2008. IEEE Symposium on (2008),
IEEE, pp. 170–183.
[4] Benko, H., Wilson, A. D., and Baudisch, P. Precise
selection techniques for multi-touch screens. In Proceedings
of the SIGCHI conference on Human Factors in computing
systems (2006), ACM, pp. 1263–1272.
[5] Cheng, N., Wang, X., Cheng, W., Mohapatra, P., and
Seneviratne, A. Characterizing privacy leakage of public
wifi networks for users on travel. In INFOCOM, 2013
Proceedings IEEE (2013), IEEE, pp. 2769–2777.
[6] Fan, Y., Jiang, Y., Zhu, H., and Shen, X. S. An efficient
privacy-preserving scheme against traffic analysis attacks in
network coding. In INFOCOM 2009, IEEE (2009), IEEE,
pp. 2213–2221.
[7] Forlines, C., Wigdor, D., Shen, C., and Balakrishnan,
R. Direct-touch vs. mouse input for tabletop displays. In
Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors
in computing systems (2007), ACM, pp. 647–656.
[8] Halperin, D., Hu, W., Sheth, A., and Wetherall, D.
Tool release: gathering 802.11 n traces with channel state
information. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication
Review 41, 1 (2011), 53–53.
[9] Hamed, K. H., and Rao, A. R. A modified mann-kendall
trend test for autocorrelated data. Journal of Hydrology
204, 1 (1998), 182–196.
[10] Holt,C.C.Forecasting seasonals and trends by
exponentially weighted moving averages. International
journal of forecasting 20, 1 (2004), 5–10.
[11] Konings, B., Bachmaier, C., Schaub, F., and Weber,
M. Device names in the wild: Investigating privacy risks of
zero configuration networking. In Mobile Data Management
(MDM), 2013 IEEE 14th International Conference on
(2013), vol. 2, IEEE, pp. 51–56.
[12] Liu,J.,Wang,Y.,Kar,G.,Chen,Y.,Yang,J.,and
Gruteser, M. Snooping keystrokes with mm-level audio
ranging on a single phone. In Proceedings of the 21st
Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing
and Networking (2015), ACM, pp. 142–154.
[13] Liu, X., Zhou, Z., Diao, W., Li, Z., and Zhang, K. When
good becomes evil: Keystroke inference with smartwatch.
In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGSAC Conference on
Computer and Communications Security (2015), ACM,
pp. 1273–1285.
[14] Lozowski, E., Charlton, R., Nguyen, C., and Wilson,
J. The use of cumulative monthly mean temperature
anomalies in the analysis of local interannual climate
variability. Journal of Climate 2, 9 (1989), 1059–1068.
[15] Mar
quardt, P., Verma, A., Carter, H., and Traynor,
P. (sp)
iphone: decoding vibrations from nearby keyboards
using mobile phone accelerometers. In Proceedings of the
18th ACM conference on Computer and communications
security (2011), ACM, pp. 551–562.
[16] Owusu, E., Han, J., Das, S., Perrig, A., and Zhang, J.
Accessory: password inference using accelerometers on
smartphones. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Workshop on
Mobile Computing Systems & Applications (2012), pp. 1–6.
[17] Sen, S., Lee, J., Kim, K.-H., and Congdon, P. Avoiding
multipath to revive inbuilding wifi localization. In
Proceeding of the 11th annual international conference on
Mobile systems, applications, and services (2013), ACM,
pp. 249–262.
[18] Shukla, D., Kumar, R., Serwadda, A., and Phoha,
V. V. Beware, your hands reveal your secrets! In
Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on
Computer and Communications Security (2014), ACM,
pp. 904–917.
[19] Sun, J., Jin, X., Chen, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, R., and
Zhang, Y. Visible: Video-assisted keystroke inference from
tablet backside motion.
[20] Wang,F.,Cao,X.,Ren,X.,andIrani,P.Detecting and
leveraging finger orientation for interaction with
direct-touch surfaces. In Proceedings of the 22nd annual
ACM symposium on User interface software and
technology (2009), ACM, pp. 23–32.
[21] Xia, N., Song, H. H., Liao, Y., Iliofotou, M., Nucci,
A., Zhang, Z.-L., and Kuzmanovic, A. Mosaic:
Quantifying privacy leakage in mobile networks. In ACM
SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review (2013),
vol. 43, ACM, pp. 279–290.
[22] Xie,Y.,Li,Z.,andLi,M.Precise power delay profiling
with commodity wifi. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual
International Conference on Mobile Computing and
Networking (New York, NY, USA, 2015), MobiCom ’15,
ACM, pp. 53–64.
[23] Yue, Q., Ling, Z., Fu, X., Liu, B., Ren, K., and Zhao,
W. Blind recognition of touched keys on mobile devices. In
Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on
Computer and Communications Security (2014), ACM,
pp. 1403–1414.
[24] Zhang, J., Zheng, X., Tang, Z., Xing, T., Chen, X.,
Fang, D., Li, R., Gong, X., and Chen, F. Privacy leakage
in mobile sensing: your unlock passwords can be leaked
through wireless hotspot functionality.
[25] Zhu, T., Ma, Q., Zhang, S., and Liu, Y. Context-free
attacks using keyboard acoustic emanations. In Proceedings
of the 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and
Communications Security (2014), ACM, pp. 453–464.
1079
**MIMO (multiple input, multiple output)** is a technique in wireless communications that allows the use of multiple antenas at the transmitter and the receiver in order to increase the throughput of the channel and minimize errors,
Alipay is an incredibly popular payment platform. In 2015 it processed 1 trillion dollars at an average of 100 million transactions a day. It was launched in China in 2004 by Alibaba and its founder Jack Ma.

The Intel 5300 NIC costs about 5 USD and the directional antenas used in the experiment cost about 20 USD. This is certainly not a costly attack.
At first it might seem that this distance requirement would make it a lot harder to actually successfully perform such attack. However, in a real world scenario it is plausible that an attacker could set the system to focus on for instance a particular table in a coffee shop.
**OFDM (Ortogonal frequency-division multiplexing)** is a method in wireless communications that encodes data on multiple carrier frequencies. Ortogonal frequencies essentially means that they do not interfere with each other. OFDM has a number of advantages such as making communication more robust against fading caused by multipath propagation.
The main idea of **Principal Component Analysis** is that you have a feature vector that describes your data (in this case Channel State Information from a number of channels - you might have multiple antenas, which communicate at a number frequencies) and you are trying to reduce the dimensionality of that feature vector to make it easier to work with.
If you wish to get a better intuition about PCA check out this [visual explanation](http://setosa.io/ev/principal-component-analysis/).
### Multipath Signals
When wireless signals propagate away from the transmitter, they can be affected by reflection, refraction or diffraction. Let’s say you have two signals (A and B) that leave the transmitter at the same time. Signal A propagates directly to the receiver. Signal B bounces off a wall before reaching the receiver. Signal B will have traveled a longer distance than signal A resulting in a phase shift which could in turn cause destructive or constructive interference.
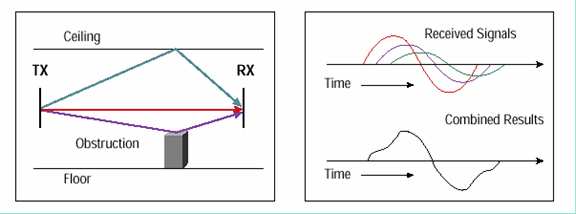
**Side-channel attacks** are attacks based on information collected from the physical implementation of a system.
Examples:
- **Power-analysis attack** - Attack that extracts information by observing the power consumption of a hardware device such as a CPU
- **Acoustic Attack** - Attack that extracts information from the sound produced by a system (e.g. movement of mechanical pieces of a device)
This seems like a particularly interesting insight. Alipay is certainly not the only service that suffers from this type of “information leak". `HTTPS` does not help you here. By just looking at the IP header you can figure out when a user is doing something particularly sensitive. This is rather valuable information for an attacker!
#### Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
ICMP is an internet protocol that is used to transmit error messages and operational information between network devices. It is widely implemented, but it is usually not employed by end-user applications to transmit data. In fact, ICMP can be used to create covert channels of communication (ICMP tunnels). [Here](https://github.com/DhavalKapil/icmptunnel) is a project that allows you to transparently tunnel your IP traffic through ICMP echo and reply packets.
Diagnostic tools like `ping` and `traceroute` make use of ICMP. When network devices forward an IP datagram they decrement the Time To Live (`TTL`) field in the IP header by one. If the `TTL` reaches 0 the IP datagram is discarded, and an ICMP `Time To Live exceeded in transit` message is sent back to the source of the datagram.
ICMP packets have an 8 byte header and a variable size data section.